5.1 Introduction to IoT Security
- IoT security is the technology area concerned with safeguarding connected devices and networks in the Internet of Things (IoT).
IoT सुरक्षा वह तकनीकी क्षेत्र है जिसमें इंटरनेट ऑफ थिंग्स (IoT) में जुड़े उपकरणों और नेटवर्क की सुरक्षा सुनिश्चित की जाती है। - IoT involves adding internet connectivity to a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals, and/or people.
IoT इंटरनेट कनेक्टिविटी को एक प्रणाली में जोड़ता है, जो आपस में जुड़े हुए कंप्यूटिंग डिवाइस, यांत्रिक और डिजिटल मशीनें, वस्तुएं, पशु और मनुष्यों से संबंधित होती है। - Each “thing” in IoT is assigned a unique identifier and has the ability to automatically transfer data over a network.
प्रत्येक “डिवाइस” को एक अद्वितीय पहचानकर्ता दिया जाता है और इसमें स्वचालित रूप से डेटा स्थानांतरित करने की क्षमता होती है। - Connecting devices to the internet exposes them to serious vulnerabilities, such as unauthorized access, malware, and data breaches, if they are not adequately protected.
उपकरणों को इंटरनेट से जोड़ने पर वे गंभीर सुरक्षा कमजोरियों के प्रति संवेदनशील हो जाते हैं, जैसे कि अनधिकृत पहुंच, मैलवेयर, और डेटा उल्लंघन, यदि उन्हें ठीक से सुरक्षित नहीं किया गया हो। - Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack is a cyberattack where a system or network is overloaded, making it unavailable to users.
डिनायल-ऑफ-सर्विस (DoS) हमला एक साइबर हमला होता है जिसमें सिस्टम या नेटवर्क को अत्यधिक ट्रैफ़िक द्वारा बाधित किया जाता है, जिससे यह उपयोगकर्ताओं के लिए अनुपलब्ध हो जाता है।
5.2 IoT Security Threats and Countermeasures
Communication Attacks-
These attacks compromise data transmitted between IoT devices and servers. Cryptography secures this information using encryption codes, ensuring only authorized persons can access it.
ये हमले डेटा को खतरे में डालते हैं, जो IoT उपकरणों और सर्वरों के बीच प्रेषित होता है। क्रिप्टोग्राफी एन्क्रिप्शन कोड का उपयोग करके इसे सुरक्षित करती है।
Lifecycle Attacks-
The integrity of an IoT device is compromised when ownership shifts from the manufacturer to the user. If security measures are weak, data or functionality may be lost.
जब स्वामित्व निर्माता से उपयोगकर्ता के पास स्थानांतरित हो जाता है, तो IoT डिवाइस की अखंडता खतरे में पड़ जाती है। यदि सुरक्षा उपाय कमज़ोर हैं, तो डेटा या कार्यक्षमता नष्ट हो सकती है।
Attacks on Device Software-
These attacks exploit system vulnerabilities to harm devices or disrupt normal operations using malicious techniques.
ये हमले सिस्टम कमजोरियों का फायदा उठाकर उपकरणों को नुकसान पहुँचाते हैं या सामान्य संचालन को बाधित करते हैं।
Physical Attacks-
Attackers physically access IoT chips to extract sensitive information, posing a security risk. Simply removing a microSD card may expose embedded passwords or private data.
हमलावर IoT चिप्स तक पहुँचकर संवेदनशील जानकारी निकाल सकते हैं, जिससे सुरक्षा जोखिम उत्पन्न होता है।
5.3 Cyber Security
Definition and Purpose
- Cyber Security focuses on protecting information technology, including computers, networks, programs, and data from unauthorized access.
साइबर सुरक्षा सूचना प्रौद्योगिकी की रक्षा पर केंद्रित होती है, जिसमें कंप्यूटर, नेटवर्क, प्रोग्राम और डेटा को अनधिकृत पहुंच से बचाना शामिल है।
Inventor and Key Dates
- Bob Thomas is considered the father of Cyber security, as he created the first computer virus, “Creeper,” in 1971.
बॉब थॉमस को साइबर सुरक्षा का जनक माना जाता है, क्योंकि उन्होंने 1971 में पहला कंप्यूटर वायरस “Creeper” बनाया था। - 1978: RSA encryption was invented by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman, forming the foundation of modern cyber security.
1978 में RSA एन्क्रिप्शन का आविष्कार रॉन रिवेस्ट, आदि शामिर और लियोनार्ड एडलमैन ने किया, जो आधुनिक साइबर सुरक्षा की नींव बना।
Importance of Cyber Security
- Cyber security protects digital assets, including devices, applications, and telecommunications systems, from Cyber threats.
साइबर सुरक्षा डिजिटल संपत्तियों, जैसे उपकरण, एप्लिकेशन और दूरसंचार प्रणालियों को साइबर खतरों से बचाती है। - It ensures safe internet usage, preventing fraud, identity theft, and cyber-attacks.
यह सुरक्षित इंटरनेट उपयोग सुनिश्चित करता है, जिससे धोखाधड़ी, पहचान की चोरी और साइबर हमलों को रोका जा सकता है।
Cyber Security Threats
- Common threats include malware, phishing, ransomware, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
प्रमुख खतरे मैलवेयर, फ़िशिंग, रैंसमवेयर और डिनायल-ऑफ-सर्विस (DoS) हमले हैं। - Cyber criminals exploit weak security systems, leading to data breaches and financial losses.
साइबर अपराधी कमजोर सुरक्षा प्रणालियों का फायदा उठाकर डेटा उल्लंघन और वित्तीय नुकसान पहुंचाते हैं।
Future of Cyber Security
- Advancements in AI, blockchain, and quantum encryption will strengthen cyber security.
AI, ब्लॉकचेन और क्वांटम एन्क्रिप्शन में प्रगति साइबर सुरक्षा को मजबूत बनाएगी। - Governments and organizations are implementing strict Cyber security regulations to protect users.
सरकारें और संगठन कड़े साइबर सुरक्षा नियम लागू कर रहे हैं ताकि उपयोगकर्ताओं की सुरक्षा सुनिश्चित की जा सके।
5.3.1 Securing Your PC
Computers have become an essential part of our daily lives. Most tasks are done online through PCs or laptops. To protect your computer from viruses, spyware, and hackers, follow these security practices:
Creating Strong and Unique Passwords
- Passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access.
- Never use default passwords; create strong passwords using uppercase, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- The stronger your password, the better protection from hackers and malware.
Keeping Windows and Devices Updated
- Choose an Operating System based on its security strength and vulnerability protection.
- Regularly update security patches and enable automatic updates for continuous protection.
- Windows has a built-in firewall that blocks unwanted Cyber intrusions.
Enabling Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- 2FA adds an extra layer of security, requiring a one-time verification code after entering your password.
- It ensures that even if passwords are compromised, attackers cannot access the device.
Installing and Updating Antivirus Software
- Install trusted antivirus software to detect ransomware, malware, and spyware before they harm your system.
- Keep your antivirus database updated to counter new Cyber threats.
Encrypting Internet Connection
- Use a VPN to encrypt your online activities, making data unreadable to cyber attackers.
- Encryption modifies data to prevent unauthorized access.
Disabling UPnP (Universal Plug and Play)
- UPnP lets devices automatically connect to networks, but it can expose them to security risks.
- Disable unused features on all devices to reduce vulnerability.
5.3.2 Securing Your Mobile
Mobile devices like smartphones and tablets are essential in daily life, but they are also vulnerable to Cyber threats. Follow these key steps to protect your device:
Protect Your Device Physically
- Use a strong password and enable auto-lock to prevent unauthorized access.
- Avoid sharing your device or passwords, as weak passwords can be easily guessed.
- Never use personal details like names, birthdays, or social security numbers in passwords.
Keep Your Data Secure
- Regularly backup and sync data to protect against unexpected loss.
- Keep your operating system updated to ensure security patches are installed.
- Never override built-in security features, as they help safeguard your device.
Safeguard Your Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
- Do not share sensitive details like bank account numbers or passwords via text.
- Always use a secure connection for mobile banking or shopping.
- Disable Geo-tagging to prevent tracking of your location.
Protect Against Malware
- Only install apps from trusted sources and read permissions before installing.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links or advertisements, as they may contain malware.
Secure Network Connections
- Use mobile data instead of public Wi-Fi when outside, as open networks can be hacked.
- Disable Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and NFC in public places when not needed.
5.4 Need for Security in IoT (IoT में सुरक्षा की आवश्यकता)
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects billions of devices, people, and services, enabling seamless data exchange. However, this interconnected network makes IoT vulnerable to cyber threats, creating a need for robust security measures. From financial transactions to smart homes, IoT devices store confidential, valuable, and sensitive data that, if compromised, can lead to severe consequences.
Security in IoT is built on the three most crucial components: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA Triad). These principles ensure data protection and system reliability.
इंटरनेट ऑफ थिंग्स (IoT) अरबों उपकरणों, लोगों और सेवाओं को जोड़ता है, जिससे निर्बाध डेटा विनिमय संभव होता है। हालांकि, यह आपस में जुड़ा नेटवर्क साइबर खतरों के प्रति संवेदनशील होता है, जिससे मजबूत सुरक्षा उपायों की आवश्यकता होती है। वित्तीय लेन-देन से लेकर स्मार्ट होम तक, IoT उपकरणों में गोपनीय, मूल्यवान और संवेदनशील डेटा संग्रहित होता है, जिसे खतरे में डालने पर गंभीर परिणाम हो सकते हैं।
IoT सुरक्षा तीन महत्वपूर्ण घटकों पर आधारित होती है: गोपनीयता (Confidentiality), अखंडता (Integrity), और उपलब्धता (Availability) – जिसे CIA त्रय (CIA Triad) कहा जाता है। ये सिद्धांत डेटा की सुरक्षा और सिस्टम की विश्वसनीयता सुनिश्चित करते हैं।
5.4.1 Confidentiality (गोपनीयता)
- Definition: Confidentiality refers to restricting unauthorized access to data while ensuring that only authorized users can view or process information.
- Importance in IoT: As data moves through multiple network hops, proper encryption mechanisms are essential to maintain confidentiality.
- Example: Data encryption protects IoT information from unauthorized disclosure, ensuring privacy.
- Threats: Hackers can intercept data transmitted across IoT networks, leading to leaks and breaches.
- परिभाषा: गोपनीयता का अर्थ है अनधिकृत उपयोगकर्ताओं से डेटा को सुरक्षित रखना, ताकि केवल अधिकृत उपयोगकर्ता ही इसकी जानकारी प्राप्त कर सकें।
- IoT में महत्व: जब डेटा अनेक नेटवर्क चरणों के माध्यम से गुजरता है, तो उचित एन्क्रिप्शन तकनीकों का उपयोग इसकी गोपनीयता बनाए रखने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
- उदाहरण: डेटा एन्क्रिप्शन IoT जानकारी को अनधिकृत प्रकटीकरण से बचाता है, जिससे इसकी गोपनीयता बनी रहती है।
- खतरे: हैकर्स नेटवर्क में भेजे गए डेटा को इंटरसेप्ट कर सकते हैं, जिससे डेटा लीक और उल्लंघन हो सकता है।
5.4.2 Integrity (अखंडता)
- Definition: Integrity ensures that data remains accurate, trustworthy, and unaltered by unauthorized users.
- Importance in IoT: Diverse IoT services, devices, and networks make stored data vulnerable to manipulation.
- Example: IoT security protocols validate data sources to prevent unauthorized changes.
- Threats: Attackers can modify stored data for malicious purposes, compromising its reliability.
- परिभाषा: अखंडता सुनिश्चित करती है कि डेटा सटीक, भरोसेमंद और अपरिवर्तित बना रहे, जिससे अनधिकृत उपयोगकर्ता इसे बदल न सकें।
- IoT में महत्व: विभिन्न IoT सेवाओं, उपकरणों और नेटवर्क के कारण संग्रहीत डेटा हेरफेर के प्रति संवेदनशील हो सकता है।
- उदाहरण: IoT सुरक्षा प्रोटोकॉल डेटा स्रोतों को सत्यापित करते हैं ताकि अनधिकृत परिवर्तन रोका जा सके।
- खतरे: हमलावर संग्रहीत डेटा को संशोधित कर सकते हैं, जिससे उसकी विश्वसनीयता और सटीकता प्रभावित हो सकती है।
5.4.3 Availability (उपलब्धता)
- Definition: Availability guarantees that authorized users can reliably access IoT systems and data whenever needed.
- Importance in IoT: IoT devices must function without disruption, providing continuous access to users.
- Example: Robust IoT security frameworks prevent service interruptions.
- Threats: Cyberattacks like Denial-of-Service (DoS) can block access to IoT services, making them unusable.
- परिभाषा: उपलब्धता यह सुनिश्चित करती है कि अधिकृत उपयोगकर्ता IoT सिस्टम और डेटा तक आसानी से पहुंच प्राप्त कर सकें।
- IoT में महत्व: IoT उपकरणों को बिना किसी रुकावट के कार्य करना चाहिए, ताकि उपयोगकर्ताओं को लगातार पहुँच मिलती रहे।
- उदाहरण: मजबूत IoT सुरक्षा ढांचे सेवाओं में व्यवधान को रोकते हैं।
- खतरे: डिनायल-ऑफ-सर्विस (DoS) हमले IoT सेवाओं तक पहुँच बाधित या अवरुद्ध कर सकते हैं।
5.5 Types of Cyber Attacks (साइबर हमलों के प्रकार)
Cyber attacks are attempts to steal, damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computers, devices, networks, or data. They are broadly classified into:
- 5.5.1 Web-based Attacks (वेब आधारित हमले)
–Injection Attack
-DNS Spoofing
-Session Hijacking
-Phishing
-Brute Force - 5.5.2 System-based Attacks (सिस्टम आधारित हमले)
–Virus
-Worm
-Trojan Horse
-Backdoors
-Bots
5.5.1 Web-based Attacks (वेब आधारित हमले)
These are the attacks that occur on websites or web applications. Some of the important web-based attacks are:-
Injection Attacks (इंजेक्शन हमला)
Injection attacks are among the oldest and most dangerous web application attacks. Injection attacks involve inserting malicious code into website inputs (like forms) to manipulate backend databases or extract unauthorized information. Injection attacks, particularly SQL injections (SQLi attacks) and Cross-site Scripting (XSS), are the most common injection attacks.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- Hackers alter student data by injecting malicious code into a college website.
हैकर कॉलेज पोर्टल में कोड डालकर छात्र रिकॉर्ड बदल देता है। - A login form on an e-commerce site is used to steal user credentials.
ई-कॉमर्स साइट का लॉगिन फॉर्म पासवर्ड चुराने के लिए इस्तेमाल होता है। - Fake form on a feedback site reveals admin login info.
फीडबैक फॉर्म दिखा कर एडमिन की जानकारी प्राप्त करना।
DNS Spoofing (डीएनएस स्पूफिंग)
In DNS Spoofing, attackers manipulate DNS responses to redirect users from real websites to fake ones.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- Banking users unknowingly visit a fake site and lose data.
बैंक की वेबसाइट की जगह उपयोगकर्ता नकली साइट खोलता है। - Public Wi-Fi redirects all traffic to malicious pages.
सार्वजनिक Wi-Fi से ब्राउज़र हानिकारक पेज पर चला जाता है। - School login portal redirects students to a phishing clone.
स्कूल की लॉगिन साइट की जगह फर्जी साइट खुल जाती है।
Session Hijacking (सेशन हाईजैकिंग)
Hijacking takes control of various parts of your web browser, including your home page, search pages, and search bar. This attack steals session IDs (stored in cookies) to impersonate a user and access their online accounts.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- Student logs in to email in a cyber café; session is hijacked.
साइबर कैफ़े में लॉगिन किया ईमेल अकाउंट हाईजैक हो गया। - Hacker takes over your Facebook while you’re still logged in.
सोशल मीडिया चलाते वक्त अकाउंट किसी और के कंट्रोल में आ गया। - Online exam sessions are hijacked to submit fake answers.
ऑनलाइन परीक्षा के दौरान सेशन चुराकर कोई और उत्तर जमा कर देता है।
Phishing (फिशिंग)
Phishing tricks users into clicking fake links or submitting private data using deceptive emails or messages. It is an attempt to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details by a hacker through an electronic communication.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- “Your ATM will be blocked”—such an email leads to fraud.
“एटीएम बंद हो जाएगा” वाले मेल से लोग लिंक पर क्लिक कर देते हैं। - Student gets a fake exam result mail asking to log in.
छात्र को नकली परीक्षा परिणाम ईमेल मिलता है। - Job seeker clicks on a fake offer letter link and enters OTP.
नौकरी की झूठी ऑफर लेटर लिंक से OTP डलवाया जाता है।
Brute Force Attack (ब्रूट फोर्स हमला)
Hackers use programs to keep guessing combinations until they crack a password or PIN.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- Someone keeps trying different PINs on a mobile banking app.
मोबाइल बैंकिंग ऐप में लगातार पासकोड ट्राय किया जाता है। - Office admin panel is repeatedly logged in using common passwords.
ऑफिस पैनल पर “admin123” जैसे पासवर्ड से बार-बार लॉगिन। - School Wi-Fi gets hacked using simple guesswork.
स्कूल वाई-फाई का आसान पासवर्ड (जैसे 12345678) ब्रेक हो जाना।
5.5.2 System-based Attacks (सिस्टम आधारित हमले)
These are the attacks that are intended to compromise a computer or a computer network. Some of the important system-based attacks are:-
Virus (वायरस)- Vital Information Resources Under Siege
A virus is a program that attaches to files and spreads across systems, often corrupting or deleting data.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- A movie downloaded from a pirated site infects the computer.
पायरेटेड साइट से मूवी डाउनलोड करने से सिस्टम संक्रमित हो गया। - Project files in a USB drive get destroyed after virus attack.
यूएसबी से प्रोजेक्ट फाइल्स गायब हो गईं। - Antivirus alerts while opening a school presentation.
स्कूल प्रजेंटेशन खोलते ही वायरस अलर्ट आ गया।
Worm (वॉर्म)- Write Once, Read Many
A worm is a self-spreading malware that can infect entire networks without user interaction.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- Hostel Wi-Fi spreads a worm across students’ laptops.
हॉस्टल Wi-Fi से छात्रों के लैपटॉप में वॉर्म फैल जाता है। - Office computers crash one after another.
ऑफिस में एक के बाद एक कंप्यूटर क्रैश हो जाते हैं। - Cyber café systems behave erratically without direct downloads.
साइबर कैफे के सिस्टम बिना कुछ डाउनलोड किए धीमे हो जाते हैं।
Trojan Horse (ट्रोजन हॉर्स)
A Trojan appears useful but secretly gives attackers remote access, steals data, or installs malware.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- A free photo editor steals files and passwords.
फोटो एडिटर दिखने वाला ऐप फाइलें और पासवर्ड चुरा लेता है। - A fake speed booster installs spyware.
पीसी स्पीड बढ़ाने वाला सॉफ्टवेयर असल में स्पाईवेयर होता है। - Students download a “notes converter” that logs keystrokes.
“नोट्स कन्वर्टर” नाम से डाउनलोड किया ऐप टाइप किए गए कीबोर्ड डिटेल्स रिकॉर्ड करता है।
Backdoor (बैकडोर)
A backdoor is a hidden access path left open in software or devices to allow unauthorized remote entry.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- Untrusted technician installs a hidden admin account.
टेक्नीशियन कंप्यूटर रिपेयर के दौरान छुपा एक्सेस दे देता है। - A cracked version of game has backdoor for hackers.
हैक की गई गेम में बैकडोर के ज़रिए हैकर एक्सेस पा लेते हैं। - Unofficial plugin in a school software gives outside access.
स्कूल के सॉफ्टवेयर में डाली गई थर्ड पार्टी प्लगइन से आउटसाइड एक्सेस हो जाता है।
Bots & Botnets (बॉट और बॉटनेट)
Bots are infected devices used for automated malicious tasks. Botnets are a network of such bots controlled by hackers.
Examples (उदाहरण):
- PC unknowingly mines cryptocurrency and overheats.
कंप्यूटर से बिना जानकारी के क्रिप्टो माइनिंग होती है और सिस्टम गर्म हो जाता है। - Botnet of smartphones floods exam site, causing downtime.
छात्रों के मोबाइल से बना बॉटनेट परीक्षा साइट को डाउन कर देता है। - Thousands of hacked cameras used to spy or spam.
हजारों हैक हुए CCTV कैमरे निगरानी या स्पैम भेजने में इस्तेमाल होते हैं।
5.6 IoT and Cyber Security Challenges
- IoT security is often neglected in the design phase, as networking appliances is a relatively new concept.
IoT सुरक्षा को डिज़ाइन के चरण में अक्सर नज़रअंदाज़ किया जाता है, क्योंकि उपकरणों को नेटवर्क से जोड़ने की अवधारणा अभी नई है। - Manufacturers prioritize launching products quickly, often ignoring strong built-in security.
निर्माता उत्पाद को जल्दी बाज़ार में लाने को प्राथमिकता देते हैं और अक्सर मजबूत आंतरिक सुरक्षा की उपेक्षा करते हैं। - Adding security from the beginning can be expensive and delay development. शुरुआत से सुरक्षा जोड़ना महंगा हो सकता है और विकास प्रक्रिया को धीमा कर सकता है।
- IoT devices often have limited hardware, making it difficult to implement advanced security tools.
IoT उपकरणों में अक्सर सीमित हार्डवेयर होता है, जिससे उन्नत सुरक्षा उपाय लागू करना कठिन हो जाता है। - In India, the rise in cyber-attacks has created an urgent demand for skilled security analysts to protect government and private sector systems.
भारत में साइबर हमलों की बढ़ती घटनाओं ने सरकारी और निजी क्षेत्र के सिस्टम को सुरक्षित रखने के लिए कुशल सुरक्षा विश्लेषकों की ज़रूरत को अत्यंत आवश्यक बना दिया है।
5.6.1 Blockchain Revolution
- Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger invented in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto.
ब्लॉकचेन एक विकेंद्रीकृत डिजिटल बहीखाता है जिसे 2008 में सातोशी नाकामोतो ने विकसित किया था। - Each transaction is recorded in a block and linked to previous blocks through cryptographic hashes.
प्रत्येक लेन-देन एक ब्लॉक में रिकॉर्ड होता है और क्रिप्टोग्राफिक हैश की मदद से पिछले ब्लॉक्स से जुड़ा होता है। - Bitcoin is the most popular cryptocurrency that uses blockchain to verify and store transactions.
बिटकॉइन सबसे प्रसिद्ध क्रिप्टोकरेंसी है जो ब्लॉकचेन का उपयोग लेन-देन की पुष्टि और संग्रह के लिए करती है। - Blockchain ensures data security, transparency, and immutability — meaning data cannot be changed once recorded.
ब्लॉकचेन डेटा की सुरक्षा, पारदर्शिता और अपरिवर्तनीयता सुनिश्चित करता है — यानी रिकॉर्ड हुआ डेटा बदला नहीं जा सकता। - It is used in various fields like finance, banking, healthcare, voting systems, and supply chain management.
इसका उपयोग वित्त, बैंकिंग, स्वास्थ्य सेवा, मतदान प्रणाली और सप्लाई चेन प्रबंधन जैसे क्षेत्रों में किया जाता है। - In India, Bitcoin is not legal tender but trading is allowed and regulated under taxation laws.
भारत में बिटकॉइन कानूनी मुद्रा नहीं है, लेकिन इसका व्यापार कर कानूनों के अंतर्गत वैध और नियंत्रित है। - Indian crypto exchanges like WazirX, CoinDCX, and ZebPay allow users to invest in blockchain-based currencies.
भारतीय क्रिप्टो एक्सचेंज जैसे वज़ीरएक्स, कॉइनडीसीएक्स और ज़ेबपे ब्लॉकचेन आधारित मुद्राओं में निवेश की सुविधा देते हैं।
5.6.2 Ransomware Evolution
- Ransomware was introduced in 1996 as “Cryptoviral Extortion” by Moti Yung and Adam Young of Columbia University.
रैंसमवेयर को 1996 में “क्रिप्टोवायरल जबरन वसूली” के रूप में मोती युंग और एडम यंग (कोलंबिया विश्वविद्यालय) द्वारा पेश किया गया था। - Their aim was to demonstrate how cryptography could be misused in cyberattacks.
उनका उद्देश्य यह दिखाना था कि क्रिप्टोग्राफी जैसी तकनीक का साइबर हमलों में दुरुपयोग कैसे हो सकता है। - Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts or blocks access to data until the victim pays a ransom.
रैंसमवेयर एक प्रकार का मैलवेयर है जो डेटा को एन्क्रिप्ट करता है या सिस्टम को लॉक कर देता है जब तक कि पीड़ित फिरौती न चुका दे। - It usually spreads through malspam (malicious spam) emails, often disguised as messages from trusted sources.
यह आमतौर पर मैलस्पैम (हानिकारक स्पैम) ईमेल के माध्यम से फैलता है, जो भरोसेमंद स्रोतों के रूप में छिपे होते हैं। - In the future, ransomware is expected to use AI and target IoT devices, increasing cyber threats globally.
भविष्य में, रैंसमवेयर से उम्मीद है कि यह आर्टिफिशियल इंटेलिजेंस (AI) का उपयोग करेगा और IoT डिवाइसों को निशाना बनाएगा, जिससे वैश्विक साइबर खतरे बढ़ेंगे।
5.6.3 IoT Threats (IoT की धमकियाँ या खतरे)
- IoT connects billions of devices but is highly vulnerable to security threats.
IoT अरबों डिवाइसों को जोड़ता है लेकिन यह सुरक्षा खतरों के प्रति बहुत संवेदनशील होता है। - Security challenges in IoT arise due to limited memory, low computing power, and battery constraints.
IoT में सुरक्षा समस्याएँ सीमित मेमोरी, कम कंप्यूटिंग पावर और बैटरी की सीमाओं के कारण होती हैं। - End-to-end data protection is essential to maintain privacy across the full data lifecycle.
पूरे डेटा जीवनचक्र में गोपनीयता बनाए रखने के लिए एंड-टू-एंड डेटा सुरक्षा आवश्यक है। - Most threats are due to user misconfiguration, so automatic security policies should be applied.
अधिकतर खतरे उपयोगकर्ता की गलत सेटिंग के कारण होते हैं, इसलिए स्वचालित सुरक्षा नीतियाँ अपनानी चाहिए।
5.6.4 AI Expansion (AI का विस्तार)
- AI and Machine Learning are transforming IT operations and security by automating processes and improving efficiency.
AI और मशीन लर्निंग IT संचालन और सुरक्षा को स्वचालित प्रक्रियाओं और दक्षता में सुधार करके बदल रहे हैं। - Organizations are increasingly adopting AI to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time.
संगठन तेजी से AI को अपनाकर साइबर खतरों का वास्तविक समय में पता लगाने और प्रतिक्रिया देने में सक्षम हो रहे हैं। - AI-powered bots can learn and adapt by downloading resources like ‘AI and Machine Learning in Your Organization’.
AI-संचालित बॉट्स ‘AI और मशीन लर्निंग इन योर ऑर्गनाइजेशन’ जैसे संसाधनों को डाउनलोड करके सीख सकते हैं और अनुकूलित हो सकते हैं। - AI is being applied in predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and automated decision-making in IT systems.
AI का उपयोग IT सिस्टम में प्रेडिक्टिव एनालिटिक्स, विसंगति का पता लगाने और स्वचालित निर्णय लेने में किया जा रहा है। - The expansion of AI is enabling smarter, faster, and more secure IT environments, reducing human intervention.
AI का विस्तार अधिक स्मार्ट, तेज़ और सुरक्षित IT वातावरण को सक्षम बना रहा है, जिससे मानव हस्तक्षेप कम हो रहा है।
5.6.5 Serverless Apps Vulnerability
- Serverless apps provide granular computing functions, saving time and reducing costs by billing in seconds instead of minutes or hours.
सर्वरलेस ऐप्स वारीक कंप्यूटिंग फंक्शन्स प्रदान करते हैं, जो समय बचाते हैं और मिनटों या घंटों के बजाय सेकंड में बिलिंग करके लागत कम करते हैं। - Rapid deployment of serverless apps can lead to inappropriate privilege levels, making them vulnerable to privilege escalation attacks.
सर्वरलेस ऐप्स की तेज़ी से तैनाती अनुचित विशेषाधिकार स्तरों का कारण बन सकती है, जिससे वे विशेषाधिकार वृद्धि हमलों के प्रति संवेदनशील हो जाते हैं। - Serverless functions often rely on external repositories, which may not be under organizational control and could introduce security risks.
सर्वरलेस फंक्शन्स अक्सर बाहरी भंडार पर निर्भर करते हैं, जो संगठन के नियंत्रण में नहीं होते और सुरक्षा जोखिम पैदा कर सकते हैं। - Attackers can identify serverless environments through URLs, potentially disrupting or disabling infrastructure externally.
हमलावर URL के माध्यम से सर्वरलेस वातावरण की पहचान कर सकते हैं और बाहरी रूप से बुनियादी ढांचे को बाधित या अक्षम कर सकते हैं। - Data in serverless apps transits through networks, making it vulnerable to interception or manipulation.
सर्वरलेस ऐप्स में डेटा नेटवर्क के माध्यम से गुजरता है, जिससे यह इंटरसेप्शन या हेरफेर के प्रति संवेदनशील हो जाता है।
5.7 Privacy for IoT-Enabled Devices
– IoT devices collect and analyze data to optimize processes and save time.
आईओटी डिवाइस डेटा इकट्ठा और विश्लेषण करके प्रक्रियाओं को बेहतर बनाते हैं और समय बचाते हैं।
– IoT has transformed industries like healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing.
आईओटी ने स्वास्थ्य, कृषि और निर्माण जैसे क्षेत्रों को बदल दिया है।
– In healthcare, IoT enables devices like heart monitors and asthma trackers to connect to the Internet.
स्वास्थ्य क्षेत्र में, आईओटी हार्ट मॉनिटर और अस्थमा ट्रैकर जैसे उपकरणों को इंटरनेट से जोड़ने में सक्षम बनाता है।
– IoT devices raise privacy and security concerns due to data sharing.
आईओटी डिवाइस डेटा साझा करने के कारण गोपनीयता और सुरक्षा संबंधी चिंताएँ बढ़ाते हैं।
5.7.1 Difficult to Encrypt
– IoT devices have weak hardware and low memory, making encryption difficult.
आईओटी डिवाइसों का हार्डवेयर कमजोर और मेमोरी कम होती है, जिससे एन्क्रिप्शन कठिन हो जाता है।
5.7.2 Lack of Experience
– Inexperienced manufacturers often create insecure IoT devices.
अनुभवहीन निर्माता अक्सर असुरक्षित आईओटी डिवाइस बनाते हैं।
– IoT programming requires expertise in kernel and OS internals, which many programmers lack.
आईओटी प्रोग्रामिंग के लिए कर्नल और ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम के आंतरिक ज्ञान की आवश्यकता होती है, जो कई प्रोग्रामर्स के पास नहीं होता।
5.7.3 Lack of Standards
– IoT security standards are still under development by organizations like NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) and IoTSF (Internet of Things Security Foundation).
IoT सुरक्षा मानक अभी भी NIST (राष्ट्रीय मानक और प्रौद्योगिकी संस्थान) और IoTSF (इंटरनेट ऑफ थिंग्स सिक्योरिटी फाउंडेशन) जैसे संगठनों द्वारा विकास के अधीन हैं।
– The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a U.S. agency that develops standards, guidelines, and best practices for cybersecurity.
राष्ट्रीय मानक एवं प्रौद्योगिकी संस्थान (एनआईएसटी) एक अमेरिकी एजेंसी है जो साइबर सुरक्षा के लिए मानक, दिशानिर्देश और सर्वोत्तम प्रथाओं का विकास करती है।
– The Internet of Things Security Foundation (IoTSF) is a non-profit, international organization focused on improving security in the connected world of IoT.
इंटरनेट ऑफ थिंग्स सिक्योरिटी फाउंडेशन (IoTSF) एक गैर-लाभकारी, अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन है जो IoT की कनेक्टेड दुनिया में सुरक्षा में सुधार लाने पर केंद्रित है।
– Without proper standards, IoT devices remain vulnerable to attacks.
सही मानकों के बिना, आईओटी डिवाइस हमलों के प्रति असुरक्षित रहते हैं।
5.7.4 Third-party IoT Vulnerabilities
– IoT devices rely on third-party components for communication and cryptography.
आईओटी डिवाइस संचार और क्रिप्टोग्राफी के लिए थर्ड-पार्टी घटकों पर निर्भर करते हैं।
– Third-party libraries often contain vulnerabilities that hackers exploit.
थर्ड-पार्टी लाइब्रेरी में अक्सर कमजोरियाँ होती हैं, जिन्हें हैकर्स एक्सप्लॉइट करते हैं।
– Many third-party components are delivered in binary form, making security evaluation difficult.
कई थर्ड-पार्टी घटक बाइनरी रूप में आते हैं, जिससे उनकी सुरक्षा का मूल्यांकन कठिन हो जाता है।
– IoT devices are prone to attacks due to dependency on insecure third-party components.
आईओटी डिवाइस असुरक्षित थर्ड-पार्टी घटकों पर निर्भरता के कारण हमलों के प्रति संवेदनशील होते हैं।
5.8 Major IoT Leaks in Global and India
5.8.1. Mirai Botnet Attack (2016)
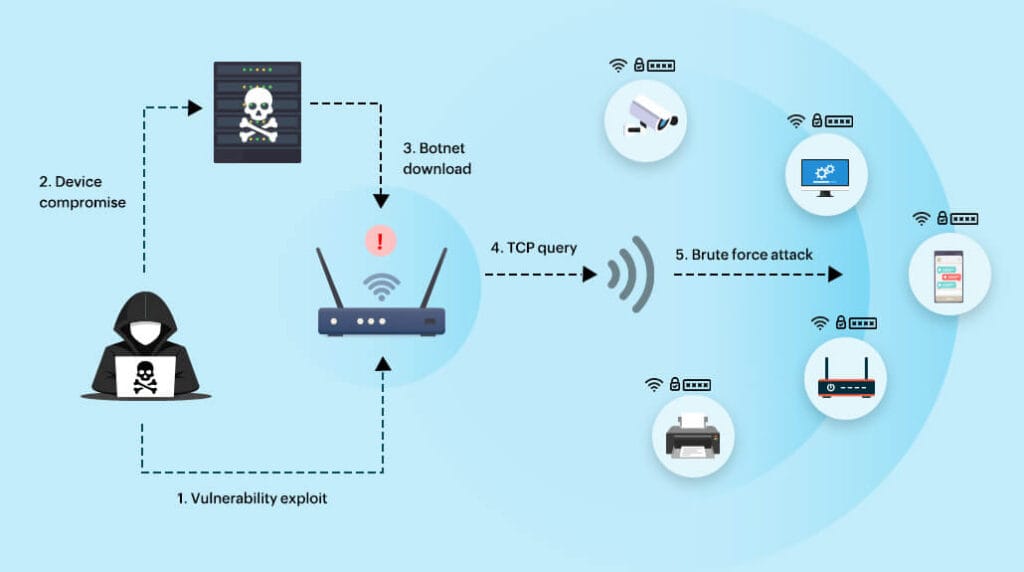
- The Mirai botnet used IoT devices to launch DDoS attacks on major platforms like Twitter, Netflix, and Amazon.
Mirai बॉटनेट ने Twitter, Netflix और Amazon जैसी प्रमुख वेबसाइटों पर DDoS हमला करने के लिए IoT डिवाइसों का इस्तेमाल किया। - It spread by scanning the Internet for devices using factory-default usernames and passwords.
यह इंटरनेट पर ऐसे डिवाइस खोजकर फैलता था जिनमें फैक्ट्री-डिफ़ॉल्ट यूज़रनेम और पासवर्ड थे।
5.8.2. Hackable Cardiac Devices (St. Jude Medical, 2017 (Global, India Impact)
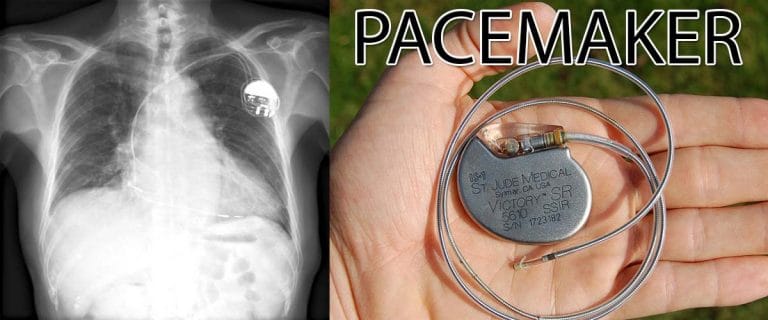
- Certain cardiac implants could be hacked and reprogrammed remotely, risking patient safety.
कुछ कार्डियक इम्प्लांट को दूर से हैक और दोबारा प्रोग्राम किया जा सकता था, जिससे मरीजों की सुरक्षा खतरे में थी। - This exposed the need for security standards in life-critical IoT healthcare devices.
यह घटना जीवन-रक्षक हेल्थकेयर IoT डिवाइसेज़ में सुरक्षा मानकों की ज़रूरत को दर
्शाती है।
5.8.3. Casino Fish Tank Thermostat Hack (2017 (Global, India Impact)
- Hackers breached a US casino’s network via a smart fish tank’s thermostat to steal internal data.
हैकर्स ने एक अमेरिकी कैसीनो के स्मार्ट फिश टैंक के थर्मोस्टेट से नेटवर्क में सेंध लगाकर अंदरूनी डेटा चुरा लिया। - This showed that even non-obvious IoT devices can become weak links in cybersecurity.
इसने साबित किया कि नज़रअंदाज़ किए गए IoT डिवाइस भी साइबर सुरक्षा की बड़ी कमजोरी बन सकते हैं।
5.8.4. VPNFilter Malware (2018 Global and India Impact)
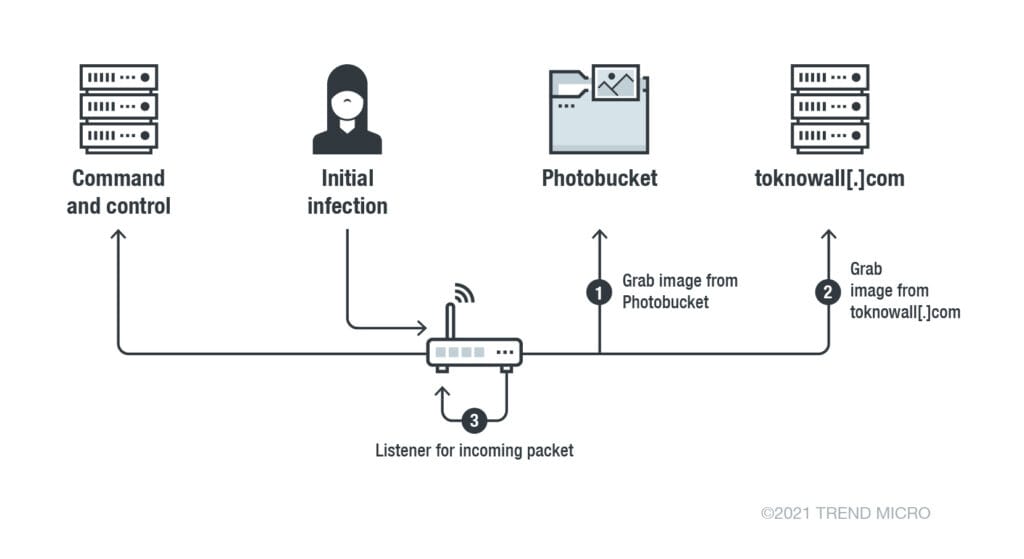
- VPNFilter infected over 500,000 routers worldwide, stealing data and blocking Internet traffic.
VPNFilter ने दुनिया भर में 5 लाख से ज़्यादा राउटर को संक्रमित कर डेटा चुराया और नेटवर्क ट्रैफ़िक को ब्लॉक किया। - The malware had modular design, allowing remote control and even device destruction. यह मैलवेयर मॉड्यूलर डिज़ाइन का था, जो दूर से डिवाइस को कंट्रोल और नष्ट करने की क्षमता रखता था।
5.8.5. Stuxnet Worm (2010)
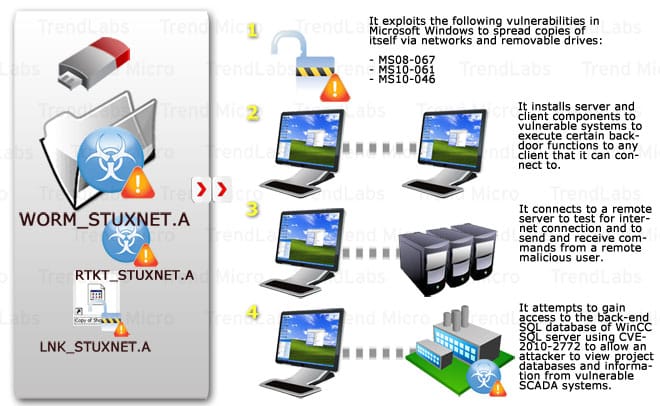
- Stuxnet was a sophisticated cyber worm that sabotaged Iran’s nuclear centrifuges via IoT-like industrial systems.
Stuxnet एक उन्नत साइबर वॉर्म था जिसने ईरान की परमाणु सेंट्रीफ्यूज को औद्योगिक IoT सिस्टम के ज़रिए नुकसान पहुँचाया। - It was among the first examples of cyber warfare targeting IoT-integrated infrastructure.
यह साइबर युद्ध का पहला उदाहरण था जिसने IoT-समेकित संरचनाओं को लक्ष्य बनाया।
5.8.6. BSNL Data Breach (2024)
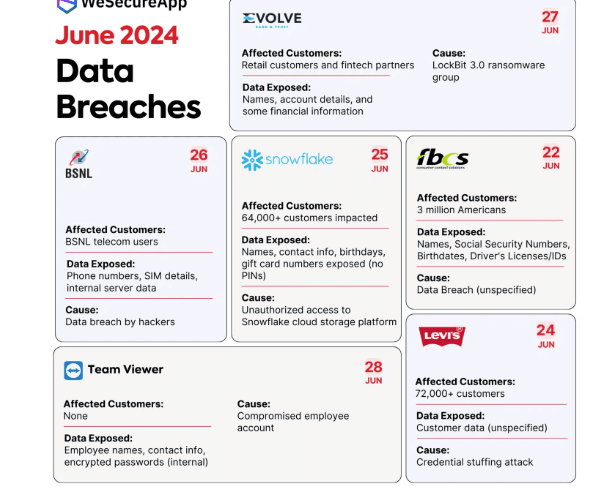
– Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) suffered a massive data breach exposing SIM card details, IMSI numbers, and server snapshots.
भारत संचार निगम लिमिटेड (BSNL) का बड़ा डेटा लीक हुआ जिसमें सिम कार्ड की जानकारी, IMSI नंबर और सर्वर की तस्वीरें उजागर हुईं।
– The breach raised concerns about how national telecom data is stored and protected in India.
इस लीक ने भारत में राष्ट्रीय टेलीकॉम डेटा की सुरक्षा और भंडारण को लेकर चिंता बढ़ा दी।
2. AIIMS Delhi Ransomware Attack (2023)

– AIIMS Delhi’s servers were hit by a ransomware attack, disrupting healthcare services and risking sensitive patient data.
एम्स दिल्ली के सर्वर पर रैनसमवेयर हमला हुआ, जिससे स्वास्थ्य सेवाएं बाधित हुईं और मरीजों का संवेदनशील डेटा खतरे में पड़ा।
– The attack exposed weaknesses in hospital IT infrastructure and emergency data recovery.
इस हमले ने अस्पताल की आईटी संरचना और आपातकालीन डेटा रिकवरी प्रणाली की कमजोरियाँ उजागर कर दीं।
5.9 Security for Consumer Devices
1. Need for Security
The rise of IoT increases risks of data theft, hacking, and misuse of consumer information.
IoT के बढ़ते उपयोग से उपभोक्ताओं की जानकारी की चोरी, हैकिंग और दुरुपयोग का खतरा बढ़ गया है।
2. Types of Consumer IoT Risks
Risks include unauthorized access, personal data leaks, malware attacks, and unsafe device behavior.
जोखिमों में अनधिकृत पहुंच, व्यक्तिगत डेटा का लीक होना, मैलवेयर अटैक और असुरक्षित डिवाइस व्यवहार शामिल हैं।
3. Importance of User Consent
Data should be collected and used only with clear user consent and transparency.
डेटा केवल स्पष्ट उपयोगकर्ता सहमति और पारदर्शिता के साथ ही एकत्र और उपयोग किया जाना चाहिए।
4. Security by Design
Devices should be built with security from the beginning, not added later.
डिवाइस को शुरुआत से ही सुरक्षा के साथ डिज़ाइन किया जाना चाहिए, न कि बाद में जोड़ा जाए।
5. Data Minimization
Only necessary data should be collected and stored to reduce risks.
केवल आवश्यक डेटा ही संग्रहित और संग्रहीत किया जाना चाहिए ताकि जोखिम कम हो।
6. Employee Awareness
Companies must train employees on cybersecurity and data protection.
कंपनियों को कर्मचारियों को साइबर सुरक्षा और डेटा सुरक्षा पर प्रशिक्षित करना चाहिए।
7. Service Provider Monitoring
External service providers must also follow strict security measures.
बाहरी सेवा प्रदाताओं को भी कड़े सुरक्षा उपायों का पालन करना चाहिए।
8. Access Control Systems
Devices should have strong access controls to prevent unauthorized usage.
डिवाइस में मजबूत एक्सेस कंट्रोल होना चाहिए ताकि अनधिकृत उपयोग रोका जा सके।
9. Patching and Updates
Known vulnerabilities must be patched regularly through software updates.
ज्ञात कमजोरियों को नियमित रूप से सॉफ़्टवेयर अपडेट द्वारा ठीक किया जाना चाहिए।
10. Consumer Responsibility
Consumers must change default passwords and install updates to stay protected.
उपभोक्ताओं को डिफ़ॉल्ट पासवर्ड बदलने और अपडेट इंस्टॉल करने चाहिए ताकि सुरक्षा बनी रहे।
5.10 Security Levels
The IoT is facing various types of attacks including active and passive attacks that may easily disturb the functionality and abolish the benefits of its services. Different types of attack, nature/behavior of attack and threat level of attacks are discussed:
| Feature | Active Attack (सक्रिय हमला) | Passive Attack (निष्क्रिय हमला) |
|---|---|---|
| Action | Data is modified or disrupted | Data is only observed or listened to |
| System Impact | System performance is affected | System runs normally |
| Detection | Easier to detect | Hard to detect |
| Goal | Damage, unauthorized control | Secret data collection |
| Example | Fake unlock command, message tampering | Eavesdropping, traffic analysis |
1. Low-Level Attack (निम्न-स्तर का हमला)
Behavior: Unsuccessful attempt to attack the network.
नेटवर्क पर हमला करने की कोशिश की गई, लेकिन वो सफल नहीं हुई।
Example: A hacker tries to ping into a smart camera’s IP but receives no response due to firewall protection.
कोई हैकर स्मार्ट कैमरा के IP को एक्सेस करने की कोशिश करता है, लेकिन फायरवॉल की वजह से कोई जवाब नहीं मिलता।
2. Medium-Level Attack (मध्यम-स्तर का हमला)
Behavior: Attacker listens to the network silently (eavesdropping), but doesn’t change data.
व्यवहार: हमलावर नेटवर्क को चुपचाप सुनता है (ईव्सड्रॉपिंग करता है), लेकिन डेटा नहीं बदलता।
Example: Intercepting communication between a fitness band and smartphone to collect step count or heart rate.
फिटनेस बैंड और स्मार्टफोन के बीच हो रहे संचार को सुनना और उसमें कदम या हार्ट रेट की जानकारी चुराना।
3. High-Level Attack (उच्च-स्तर का हमला)
Behavior: Attacker modifies or corrupts the transmitted data — affects data integrity.
हमलावर भेजे जा रहे डेटा को बदल देता है या उसे बिगाड़ देता है — डेटा की अखंडता पर असर पड़ता है।
Example: Altering the temperature data sent from a smart thermostat, leading to false readings.
स्मार्ट थर्मोस्टेट से भेजे जा रहे तापमान डेटा को बदल देना, जिससे गलत रीडिंग मिलती है।
4. Extremely High-Level Attack (अत्यधिक उच्च-स्तर का हमला)
Behavior: Full system compromise — unauthorized access, network jamming, illegal operations.
पूरा सिस्टम हैक हो जाता है — अनधिकृत पहुंच, नेटवर्क जाम करना या अवैध काम करना।
Example: Using malware to gain full control of home routers and using them in botnet attacks (like Mirai).
मैलवेयर से होम राउटर को पूरी तरह हैक करके उसे बॉटनेट अटैक के लिए इस्तेमाल करना (जैसे Mirai बॉटनेट में हुआ था)।
5.11Protecting IoT Devices
IoT डिवाइसेज़ की सुरक्षा
1. Build Security from the Start
Security should be included during device design, not after deployment.
सुरक्षा को डिवाइस के डिज़ाइन के समय से ही शामिल किया जाना चाहिए, न कि बाद में। Example: A smart bulb with encrypted firmware from the beginning.
2. Avoid Default or Hardcoded Passwords
Devices should not have fixed usernames/passwords like “admin:admin”.
डिवाइस में तयशुदा (डिफ़ॉल्ट) यूज़रनेम/पासवर्ड नहीं होने चाहिए।
Example: Camera system asks user to set new password before use.
3. Update Firmware and Software Regularly
Ensure timely updates to fix vulnerabilities.
कमजोरियों को दूर करने के लिए नियमित अपडेट ज़रूरी हैं।
Example: Router patch to fix Wi-Fi encryption bug.
4. Use Strong Encryption
Encrypt data in transit and at rest using robust algorithms.
डेटा को स्थानांतरण और संग्रह दोनों समय पर एन्क्रिप्ट करें।
Example: Smartwatch sends health data via HTTPS.
5. Implement Multifactor Authentication
Use biometrics or OTP in addition to passwords.
पासवर्ड के साथ बायोमेट्रिक्स या OTP जैसे सुरक्षा उपाय अपनाएं।
Example: Smart lock asks for fingerprint + PIN.
6. Use Secure Boot & Full-Disk Encryption
Devices should only run trusted software during boot-up.
डिवाइस को केवल भरोसेमंद सॉफ़्टवेयर से बूट होना चाहिए।
Example: IoT device with Secure Boot like Windows 10 IoT + BitLocker.
7. Network Segmentation
Keep IoT devices in separate networks to limit exposure.
IoT डिवाइसेज़ को अलग नेटवर्क में रखें ताकि खतरा सीमित हो।
Example: Smart TV connected to the guest Wi-Fi network.
8. Implement API and PKI Security
Only authorized apps should interact with devices using secure certificates.
केवल अधिकृत ऐप ही PKI या डिजिटल सर्टिफिकेट के ज़रिए डिवाइस से संपर्क करें।
Example: Secure authentication for mobile app controlling home automation.
9. Use Firewalls and Monitoring Systems
Use IDS, IPS, and firewalls to detect and block threats.
हमलों का पता लगाने और उन्हें रोकने के लिए IDS, IPS और फायरवॉल का उपयोग करें।
Example: Gateway firewall detects botnet attempts on connected camera.
10. Educate Users & Consumers
Teach users to change passwords and apply updates.
उपयोगकर्ताओं को पासवर्ड बदलने और अपडेट करने की जानकारी दें।
Example: Notification reminds users to install firmware patch.
5.12 Future IoT Ecosystem
भविष्य का IoT इकोसिस्टम
1. Seamless Connectivity with Any Device, Anytime
In future, IoT will allow people and devices to connect anytime, anywhere, using any network.
भविष्य में IoT लोगों और डिवाइसेज़ को किसी भी समय, किसी भी स्थान से, किसी भी नेटवर्क के माध्यम से जोड़ने में सक्षम बनाएगा।
Example: एक स्मार्ट हेल्थ बैंड जो दुनिया के किसी भी हिस्से से डॉक्टर को डेटा भेज सकेगा।
2. Transformation of Lifestyles and Business Models
IoT will change the way we live and work by automating homes, industries, and public services.
IoT हमारे रहने और काम करने के तरीके को बदल देगा — जैसे घर, उद्योग और सार्वजनिक सेवाओं को स्वचालित बना देगा।
Example: स्मार्ट होम, जहाँ एसी, लाइट्स और गेट्स सभी app से कंट्रोल हों।
3. Billions of Devices Sharing Information
Billions of devices, people, and services will be interconnected, exchanging real-time data.
अरबों डिवाइस, लोग और सेवाएँ एक-दूसरे से जुड़ी होंगी और वास्तविक समय में डेटा साझा करेंगी
Example: स्मार्ट खेती में सेंसर खेत की नमी और तापमान सीधे किसान को बताएंगे।
4. Need for Strong Privacy and Security Protocols
With more devices, IoT networks will face more cyberattacks — needing encryption, access control, and authentication.
अधिक डिवाइस होने के कारण IoT नेटवर्क साइबर हमलों के लिए अधिक संवेदनशील होंगे — जिससे एन्क्रिप्शन, एक्सेस कंट्रोल और प्रमाणीकरण जरूरी होंगे।
Example: स्मार्ट कैमरा को एक्सेस करने से पहले फेस रिकग्निशन + पासवर्ड की आवश्यकता।
5. Self-identifying Smart Devices
In future, IoT devices will identify and authenticate themselves with other devices automatically.
भविष्य में IoT डिवाइस अपने आप एक-दूसरे को पहचानेंगे और प्रमाणित करेंगे।
Example: एक स्मार्ट प्रिंटर नेटवर्क में खुद को रजिस्टर कर लेगा जब नया लैपटॉप कनेक्ट होगा।
6. Use of RFID and QR Codes for Communication
Technologies like RFID and QR codes will help devices share data faster and more efficiently.
RFID और QR कोड जैसी तकनीकें डिवाइसों को तेज़ और प्रभावी डेटा संचार में मदद करेंगी
Example: एक वेयरहाउस में प्रत्येक पैकेट का RFID स्कैन कर सिस्टम उसका लोकेशन और स्टेटस जानता रहेगा।
7. IoT in Logistics and Supply Chain
IoT and RFID will help industries forecast trends, detect risks, and manage supply chains smartly.
IoT और RFID उद्योगों को प्रवृत्तियों का पूर्वानुमान लगाने, जोखिम पहचानने और आपूर्ति श्रृंखला को स्मार्ट तरीके से प्रबंधित करने में मदद करेंगे।
Example: ट्रक के IoT सेंसर खराब मौसम का पता लगाकर वैकल्पिक रास्ते का सुझाव देंगे।
5.13.1 What is Cryptography?
क्रिप्टोग्राफी क्या है?
1. Definition (परिभाषा)
- Cryptography is the scientific method of protecting sensitive information by converting it into unreadable format (ciphertext) and then converting it back to readable format (plaintext) when needed. क्रिप्टोग्राफी एक वैज्ञानिक विधि है जो संवेदनशील जानकारी को सुरक्षा देने के लिए उसे अपठनीय रूप (साइफरटेक्स्ट) में बदलती है और आवश्यकता पड़ने पर फिर से पठनीय (प्लेनटेक्स्ट) रूप में बदल देती है।
Goals of Cryptography | क्रिप्टोग्राफी के उद्देश्य
1. Confidentiality (गोपनीयता)
- Ensuring that information is only accessible to authorized users. यह सुनिश्चित करना कि जानकारी केवल अधिकृत उपयोगकर्ताओं के लिए ही उपलब्ध हो।
Example: Bank transaction details should be visible only to the customer and the bank.
2. Integrity (अखंडता)
- Protecting data from being altered or tampered with during transmission or storage. डेटा को इस प्रकार सुरक्षित रखना कि उसमें किसी प्रकार का बदलाव न किया जा सके।
Example: If a medical report is sent to a doctor, its contents must remain unchanged.
3. Authentication (प्रमाणीकरण)
- Verifying the identity of the sender or source of the message. यह सत्यापित करना कि संदेश भेजने वाला व्यक्ति वही है जो वह दावा करता है।
Example: Logging into an email using a password or fingerprint.
4. Non-repudiation (इनकार-अयोग्यता)
- Ensuring that the sender cannot deny sending the message or transaction. यह सुनिश्चित करना कि संदेश भेजने वाला बाद में यह न कह सके कि उसने वह नहीं भेजा।
Example: A digitally signed agreement sent over email cannot be denied later.
Related Fields of Cryptography
क्रिप्टोग्राफी से संबंधित क्षेत्र
1. Cryptology (क्रिप्टोलॉजी)
Cryptology is the mathematical foundation of cryptography. It includes the development of algorithms, number theory, and mathematical formulas used to secure data.
क्रिप्टोलॉजी क्रिप्टोग्राफी की गणितीय नींव है। इसमें डेटा की सुरक्षा हेतु एल्गोरिद्म, संख्यात्मक सिद्धांत और सूत्रों का विकास किया जाता है।
– It combines both cryptography and cryptanalysis.
2. Cryptanalysis (क्रिप्टएनालिसिस)
Cryptanalysis is the study of cipher systems to identify weaknesses and retrieve original plaintext without knowing the key.
क्रिप्टएनालिसिस सिफर प्रणालियों की जांच है, जिससे उनकी कमजोरियों को पहचानकर बिना कुंजी के मूल जानकारी प्राप्त की जा सके।
Example: Breaking a password-protected message by analyzing the cipher pattern.
| विशेषता (Feature) | Symmetric Key (सममिति कुंजी) | Asymmetric Key (विषम कुंजी) |
|---|---|---|
| कुंजी की संख्या (Number of Keys) | एक ही कुंजी — Encryption और Decryption दोनों के लिए। One key used for both encryption and decryption | दो कुंजी — Public Key (Encrypt), Private Key (Decrypt)। Two keys — one for encryption, one for decryption |
| गति (Speed) | तेज़ और कम संसाधन उपयोग करता है। Faster and uses fewer resources | धीमा होता है, क्योंकि गणना भारी होती है। Slower due to complex computations |
| सुरक्षा (Security) | कुंजी अगर लीक हो जाए तो पूरा सिस्टम असुरक्षित हो जाता है। If the key is leaked, the system is compromised | अधिक सुरक्षित — अलग-अलग कुंजी उपयोग में लाना इसे मजबूत बनाता है। More secure due to separate keys |
| उपयोग (Usage) | थोक डेटा एन्क्रिप्शन, VPN, डिस्क/फ़ाइल एन्क्रिप्शन। Bulk data encryption, VPNs, disk/file encryption. | सुरक्षित कुंजी विनिमय, डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर, ईमेल एन्क्रिप्शन। Secure key exchange, digital signatures, email encryption. |
| उदाहरण (Examples) | AES, DES, RC4 | RSA, ECC, ElGamal |
5.13.3 Top 5 Important Cryptographic Algorithms
1️. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- A fast and secure symmetric key encryption algorithm used worldwide.
तेज़ और सुरक्षित symmetric key एल्गोरिद्म जो दुनियाभर में उपयोग किया जाता है।
Used in: Wi-Fi security (WPA2/WPA3), mobile apps, file encryption
2. RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman)
- Asymmetric encryption algorithm using a public-private key pair for secure communication.
सार्वजनिक और निजी कुंजी पर आधारित विषम कुंजी एल्गोरिद्म — सुरक्षित संचार के लिए।
Used in: Secure email, digital signatures, SSL/TLS certificates
3. SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm – 256 bit)
- One-way hashing algorithm used for verifying data integrity.
डेटा की अखंडता की पुष्टि करने के लिए प्रयुक्त एक दिशा वाली हैशिंग एल्गोरिद्म
Used in: Blockchain, file verification, password hashing
4. DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm)
- Used to digitally sign data, ensuring authenticity and non-repudiation.
डिजिटल सिग्नेचर करने के लिए प्रयोग होता है, जिससे प्रमाणीकरण और इनकार-अयोग्यता सुनिश्चित होती है।
Used in: E-governance documents, Aadhaar authentication, legal e-documents
5. ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
- Lightweight asymmetric algorithm suitable for IoT and mobile devices due to smaller key size and efficiency.
कम कुंजी आकार और दक्षता के कारण IoT और मोबाइल के लिए उपयुक्त विषम कुंजी एल्गोरिद्म।
Used in: Smart cards, cryptocurrencies, IoT device authentication
5.14 Examples of New Trends
Today, you are dependent on technologies. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) are among the technologies that have great scope and prospects for the future.
5.15 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता
Artificial Intelligence is a branch of computer science that aims to create systems or machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, decision-making, problem-solving, and understanding language.
कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता कंप्यूटर विज्ञान की वह शाखा है जिसका उद्देश्य ऐसे सिस्टम या मशीनें बनाना है जो इंसानों जैसी बुद्धिमत्ता से कार्य कर सकें, जैसे सीखना, निर्णय लेना, समस्या हल करना और भाषा को समझना।
Example:
- Siri, Alexa
- Self-driving cars
- Face recognition in phones
1. Machine Learning (ML) | मशीन लर्निंग
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
मशीन लर्निंग, AI की एक शाखा है जो कंप्यूटर को डेटा से सीखने और अनुभव से सुधार करने की क्षमता देती है, बिना उन्हें विशेष रूप से प्रोग्राम किए।
Example:
- Netflix recommending shows
- Gmail spam filter
- Online fraud detection
2. Neural Network | न्यूरल नेटवर्क
A Neural Network is a system of algorithms modeled after the human brain that helps machines recognize patterns and solve complex problems.
न्यूरल नेटवर्क एक ऐसा सिस्टम है जो मानव मस्तिष्क की तरह कार्य करता है और मशीन को पैटर्न पहचानने और जटिल समस्याओं को हल करने में मदद करता है।
Example:
- Handwriting recognition
- Image classification
- Speech-to-text converters
3. Deep Learning | डीप लर्निंग
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that uses multiple layers of neural networks to analyze various levels of features in data.
डीप लर्निंग, मशीन लर्निंग की एक शाखा है जिसमें कई स्तरों वाले न्यूरल नेटवर्क का उपयोग करके डेटा की गहराई से विश्लेषण किया जाता है।
Example:
- Self-driving cars recognizing pedestrians
- Deepfake videos
- Advanced voice assistants
4. Computer Vision | कंप्यूटर विज़न
Computer Vision is the field of AI that enables computers to interpret and understand visual information from the world.
कंप्यूटर विज़न, AI का वह क्षेत्र है जिसमें कंप्यूटर को कैमरा या तस्वीरों से प्राप्त दृश्य जानकारी को समझने और विश्लेषण करने की क्षमता दी जाती है।
Example:
- Face detection in photos
- Barcode scanner apps
- Traffic sign recognition in autonomous cars
5. Natural Language Processing (NLP) | प्राकृतिक भाषा प्रसंस्करण
NLP is the ability of a machine to understand, interpret, and respond to human language (text or speech) in a meaningful way.
प्राकृतिक भाषा प्रसंस्करण एक तकनीक है जिससे मशीनें इंसानी भाषा (लिखित या बोली हुई) को समझती, विश्लेषण करती और उसका उत्तर देती हैं।
Example:
- Google Translate
- ChatGPT / virtual assistants
- Sentiment analysis (e.g., analyzing tweet emotions)
5.15.1 Applications of AI (एआई के अनुप्रयोग)
- Gaming
- Chatbot and Voice Assistant
- Medical Diagnostics
- Fashion and Shopping Recommendation
- Industry Manufacturing
- Education
- Smart Assistant
- Automotive
5.15.2 Advantages of AI (AI के लाभ)
1. High Accuracy and Precision in Work
(कार्य में उच्च सटीकता और शुद्धता)
AI systems can perform calculations or diagnoses with near-perfect accuracy.
उदाहरण (Example):
In medical imaging (MRI, CT Scan), AI detects tumors more accurately than humans.
मेडिकल इमेजिंग (जैसे MRI) में AI ट्यूमर की पहचान डॉक्टरों से ज़्यादा सटीकता से करता है।
2. 24×7 Availability Without Fatigue
(थकान के बिना 24×7 कार्य करने की क्षमता)
AI doesn’t need breaks or rest like humans. It can function all day and night.
उदाहरण (Example):
Customer care chatbots on websites are available 24/7.
वेबसाइट पर चैटबॉट दिन-रात 24 घंटे ग्राहकों की सहायता करते हैं।
3. Efficiency in Repetitive and Routine Tasks
(दोहराए जाने वाले कार्यों में दक्षता)
AI automates routine tasks like form filling, sorting emails, or quality control.
उदाहरण (Example):
Amazon uses AI to automatically sort and pack millions of orders daily.
Amazon अपने गोदामों में रोज़ लाखों ऑर्डर AI द्वारा सॉर्ट और पैक करता है।
4. Faster and Smarter Decision Making
(तेज़ और स्मार्ट निर्णय लेने की क्षमता)
AI can make fast decisions based on real-time data analysis.
उदाहरण (Example):
Stock trading apps use AI to buy/sell shares in milliseconds.
शेयर बाजार में ट्रेडिंग ऐप्स AI से सेकंडों में शेयर खरीद-बेच करते हैं।
5. Intelligent Virtual Assistants
(बुद्धिमान वर्चुअल सहायक)
AI assistants help users via voice commands or smart devices.
उदाहरण (Example):
“Alexa, turn off the lights” – your lights turn off instantly.
“Alexa, पंखा चालू करो” – और पंखा अपने आप चालू हो जाता है।
6. Handling Massive Amounts of Data
(बड़े डेटा का तेज़ प्रबंधन)
AI can quickly process data for analysis and insights.
उदाहरण (Example):
Google Search Engine uses AI to deliver search results in milliseconds.
Google AI का उपयोग करके सेकंडों में करोड़ों डेटा से सबसे सटीक परिणाम दिखाता है।
7. Use in Dangerous or Risky Environments
(खतरनाक परिस्थितियों में उपयोग)
AI-based robots are deployed where human life is at risk.
उदाहरण (Example):
NASA uses AI robots for space missions (e.g., Mars Rover).
NASA ने मंगल ग्रह पर रोबोट भेजे जो AI से नियंत्रित हैं।
8. Personalized Recommendations and Services
(व्यक्तिगत सुझाव और अनुभव)
AI suggests products, videos, or services based on user behavior.
उदाहरण (Example):
Netflix recommends shows based on your watch history.
Netflix आपके देखे गए शो के अनुसार नए शो का सुझाव देता है।
5.15.3 Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence (AI के नुकसान)
1. High Implementation Cost
(उच्च लागत पर कार्यान्वयन)
Developing and maintaining AI systems is very expensive.
Example: AI-powered robots in manufacturing plants require costly hardware and software.
उदाहरण: AI रोबोट्स का उपयोग फैक्ट्री में करने के लिए भारी निवेश की ज़रूरत होती है।
2. Unemployment due to Automation
(स्वचालन के कारण बेरोजगारी)
AI replaces human jobs, especially in repetitive task roles.
Example: Automated checkouts in supermarkets reduce the need for human cashiers.
उदाहरण: सुपरमार्केट में सेल्फ-चेकआउट मशीनें मानव कैशियर की जगह ले रही हैं।
3. Lack of Human Emotion and Ethics
(भावनाओं और नैतिकता की कमी)
AI cannot understand or replicate true human emotions, empathy, or moral judgment.
Example: AI may reject a loan application purely on data, not on human need.
उदाहरण: बैंक में AI केवल डेटा देखकर ऋण अस्वीकार कर सकता है, भावनाओं को नहीं समझ सकता।
4. Risk of Malfunction or Errors
(गड़बड़ी या त्रुटियों का खतरा)
AI errors can lead to big losses or even disasters.
Example: An AI-based self-driving car misinterpreting signals can cause accidents.
उदाहरण: AI पर आधारित सेल्फ-ड्राइविंग कार गलत संकेत पहचानकर दुर्घटना कर सकती है।
5.Security and Privacy Concerns
(सुरक्षा और गोपनीयता की समस्याएँ)
AI can be misused to track, hack, or spy on people.
Example: AI-powered facial recognition systems raise surveillance issues.
उदाहरण: चेहरे की पहचान करने वाले AI सिस्टम गोपनीयता का उल्लंघन कर सकते हैं।
6. Dependency on Machines
(मशीनों पर अत्यधिक निर्भरता)
Overuse of AI may make humans lazy or too dependent on technology.
Example: Students using AI tools for all tasks may stop thinking critically.
उदाहरण: छात्र अगर हर काम के लिए AI का इस्तेमाल करेंगे तो उनका स्वयं का सोचने का तरीका कमज़ोर होगा।
7. Bias in AI Algorithms
(AI एल्गोरिदम में पक्षपात)
AI systems can be biased if trained on biased data.
Example: A hiring tool trained on past male-dominated data may reject qualified female candidates.
उदाहरण: भर्ती के लिए AI टूल अगर पूर्वाग्रही डेटा से प्रशिक्षित है तो योग्य उम्मीदवारों को भी अस्वीकार कर सकता है।0
5.15.4 Types of AI based on Capabilities / क्षमताओं के आधार पर AI के प्रकार
This classification describes how intelligent an AI system is compared to human intelligence.
1. Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
2. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
3. Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
1. Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) / संकीर्ण कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता (ANI)
Also known as “Weak AI,” ANI is designed and trained for a specific, narrow task. It operates within a predefined range and cannot perform outside its programmed function. Most of the AI we interact with today falls into this category.
इसे “कमजोर AI” भी कहा जाता है, ANI को किसी विशिष्ट, संकीर्ण कार्य के लिए डिज़ाइन और प्रशिक्षित किया जाता है। यह एक पूर्व-निर्धारित दायरे में काम करता है और अपने प्रोग्राम किए गए कार्य के बाहर प्रदर्शन नहीं कर सकता है। आज हम जिस अधिकांश AI से बातचीत करते हैं, वह इसी श्रेणी में आता है।
Examples / उदाहरण:
- Voice Assistants (Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa): They can understand and respond to voice commands for specific tasks like setting alarms, playing music, or answering simple questions, but they don’t have general human intelligence.
- Recommendation Systems (Netflix, Amazon): They suggest movies, products, or music based on your past preferences and behavior, but they can’t perform other tasks like driving a car.
- Spam Filters: They identify and filter out unwanted emails based on learned patterns.
- Chess-playing AI (e.g., IBM’s Deep Blue): It can play chess at a superhuman level but cannot perform any other intellectual task.
2. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) / सामान्य कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता (AGI)
Also known as “Strong AI” or “Human-Level AI,” AGI aims to possess cognitive abilities similar to a human being. It would be able to understand, learn, and apply intelligence to solve any intellectual task that a human can. AGI is still largely a theoretical concept and a subject of ongoing research.
इसे “मजबूत AI” या “मानव-स्तरीय AI” भी कहा जाता है, AGI का लक्ष्य मानव के समान संज्ञानात्मक क्षमताओं को प्राप्त करना है। यह किसी भी बौद्धिक कार्य को समझने, सीखने और बुद्धि का उपयोग करने में सक्षम होगा जो एक इंसान कर सकता है। AGI अभी भी बड़े पैमाने पर एक सैद्धांतिक अवधारणा है और चल रहे शोध का विषय है।
Examples / उदाहरण:
- There are currently no true examples of AGI in existence. It would be an AI capable of performing diverse tasks like writing a novel, conducting scientific research, solving complex mathematical problems, and engaging in philosophical debate, all with human-level understanding and adaptability.
- वर्तमान में AGI का कोई वास्तविक उदाहरण मौजूद नहीं है। यह एक ऐसा AI होगा जो मानव-स्तर की समझ और अनुकूलनशीलता के साथ एक उपन्यास लिखने, वैज्ञानिक अनुसंधान करने, जटिल गणितीय समस्याओं को हल करने और दार्शनिक बहस में शामिल होने जैसे विविध कार्य करने में सक्षम होगा।
3. Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) / सुपर कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता (ASI)
ASI is a hypothetical level of AI that would surpass human intelligence in every aspect, including creativity, general knowledge, and problem-solving abilities. It would be capable of performing tasks that humans can’t, or can’t do as well, across all domains. ASI remains purely speculative and is often discussed in the context of future AI scenarios and their potential impact.
ASI AI का एक काल्पनिक स्तर है जो रचनात्मकता, सामान्य ज्ञान और समस्या-समाधान क्षमताओं सहित हर पहलू में मानव बुद्धि को पार कर जाएगा। यह ऐसे कार्य करने में सक्षम होगा जो मनुष्य नहीं कर सकते, या सभी डोमेन में उतनी अच्छी तरह से नहीं कर सकते। ASI पूरी तरह से सट्टा बना हुआ है और अक्सर भविष्य के AI परिदृश्यों और उनके संभावित प्रभाव के संदर्भ में चर्चा की जाती है।
Examples / उदाहरण:
- This is purely speculative, but an ASI could potentially design entirely new forms of technology, solve world hunger, or even develop new scientific theories beyond human comprehension.
यह विशुद्ध रूप से सट्टा है, लेकिन एक ASI संभावित रूप से प्रौद्योगिकी के पूरी तरह से नए रूपों को डिजाइन कर सकता है, विश्व की भूख को हल कर सकता है, या यहां तक कि मानव समझ से परे नए वैज्ञानिक सिद्धांतों को विकसित कर सकता है।
Types of AI based on Functionality / कार्यप्रणाली के आधार पर AI के प्रकार
This classification describes how an AI system functions and its level of cognitive ability.
1. Reactive Machines / प्रतिक्रियाशील मशीनें
- English: These are the most basic types of AI. They react to current situations without any memory of past experiences or the ability to learn. They cannot form a complete understanding of the world.
- Hindi: ये AI के सबसे बुनियादी प्रकार हैं। वे पिछली अनुभवों की किसी भी स्मृति या सीखने की क्षमता के बिना वर्तमान स्थितियों पर प्रतिक्रिया करते हैं। वे दुनिया की पूरी समझ नहीं बना सकते।
- Examples / उदाहरण:
- English:
- IBM’s Deep Blue: The chess-playing computer that beat Garry Kasparov. It could identify pieces on the chessboard and predict moves, but it had no memory of past games and couldn’t learn from them beyond its current game state.
- Spam filters (basic): Some early spam filters simply reacted to keywords without learning over time.
- Hindi:
- IBM का डीप ब्लू: शतरंज खेलने वाला कंप्यूटर जिसने गैरी कास्पारोव को हराया था। यह शतरंज की बिसात पर टुकड़ों की पहचान कर सकता था और चालों की भविष्यवाणी कर सकता था, लेकिन उसके पास पिछले खेलों की कोई स्मृति नहीं थी और वह अपनी वर्तमान खेल स्थिति से परे उनसे सीख नहीं सकता था।
- स्पैम फिल्टर (मूलभूत): कुछ शुरुआती स्पैम फिल्टर समय के साथ सीखे बिना केवल कीवर्ड पर प्रतिक्रिया करते थे।
- English:
2. Limited Memory AI / सीमित स्मृति AI
- English: These AI systems can use past experiences or data to make informed decisions for a short period. They have a “limited memory” of previous events, which helps them make better predictions than reactive machines. Most of the AI we use today falls into this category.
- Hindi: ये AI सिस्टम कम समय के लिए सूचित निर्णय लेने के लिए पिछली अनुभवों या डेटा का उपयोग कर सकते हैं। उनके पास पिछली घटनाओं की “सीमित स्मृति” होती है, जो उन्हें प्रतिक्रियाशील मशीनों की तुलना में बेहतर भविष्यवाणियां करने में मदद करती है। आज हम जिस अधिकांश AI का उपयोग करते हैं, वह इसी श्रेणी में आता है।
- Examples / उदाहरण:
- English:
- Self-driving cars: They store recent observations of their surroundings (e.g., speed of nearby cars, distance from other objects) to make immediate driving decisions. They don’t store an entire lifetime of driving experiences.
- Recommendation engines: While they use past user data, they typically focus on recent interactions to provide relevant suggestions.
- Hindi:
- सेल्फ-ड्राइविंग कारें: वे अपने परिवेश की हाल की टिप्पणियों (जैसे, पास की कारों की गति, अन्य वस्तुओं से दूरी) को तत्काल ड्राइविंग निर्णय लेने के लिए संग्रहीत करती हैं। वे ड्राइविंग अनुभवों का पूरा जीवनकाल संग्रहीत नहीं करती हैं।
- सिफारिश इंजन: हालांकि वे पिछले उपयोगकर्ता डेटा का उपयोग करते हैं, वे आमतौर पर प्रासंगिक सुझाव प्रदान करने के लिए हाल की बातचीत पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं।
- English:
3. Theory of Mind AI / माइंड AI का सिद्धांत
- English: This type of AI is still largely in the research and development phase. It refers to AI systems that can understand emotions, beliefs, intentions, and desires, not just of humans but also of other AI systems. This would require the AI to possess social intelligence.
- Hindi: इस प्रकार का AI अभी भी बड़े पैमाने पर अनुसंधान और विकास के चरण में है। यह उन AI प्रणालियों को संदर्भित करता है जो न केवल मनुष्यों बल्कि अन्य AI प्रणालियों की भावनाओं, विश्वासों, इरादों और इच्छाओं को समझ सकते हैं। इसके लिए AI में सामाजिक बुद्धिमत्ता का होना आवश्यक होगा।
- Examples / उदाहरण:
- English: No fully realized examples exist. Potential applications could include highly empathetic AI companions, advanced negotiation systems, or AI capable of understanding subtle human cues in complex social interactions.
- Hindi: कोई पूरी तरह से महसूस किए गए उदाहरण मौजूद नहीं हैं। संभावित अनुप्रयोगों में अत्यधिक सहानुभूति वाले AI साथी, उन्नत वार्ता प्रणाली, या जटिल सामाजिक बातचीत में सूक्ष्म मानवीय संकेतों को समझने में सक्षम AI शामिल हो सकते हैं।
4. Self-Aware AI / आत्म-जागरूक AI
- English: This is the most advanced and currently purely hypothetical type of AI. Self-aware AI would possess consciousness, self-awareness, and sentience, meaning it would be aware of its own existence, feelings, and understanding. This concept is often explored in science fiction.
- Hindi: यह AI का सबसे उन्नत और वर्तमान में विशुद्ध रूप से काल्पनिक प्रकार है। आत्म-जागरूक AI में चेतना, आत्म-जागरूकता और संवेदनशीलता होगी, जिसका अर्थ है कि वह अपने अस्तित्व, भावनाओं और समझ के बारे में जागरूक होगा। इस अवधारणा को अक्सर विज्ञान कथाओं में खोजा जाता है।
- Examples / उदाहरण:
- English: There are no real-world examples of self-aware AI. This is the realm of science fiction, such as sentient robots in movies like “Blade Runner” or “Ex Machina.”
- Hindi: आत्म-जागरूक AI के कोई वास्तविक दुनिया के उदाहरण नहीं हैं। यह विज्ञान कथा का क्षेत्र है, जैसे “ब्लेड रनर” या “एक्स मशीन” जैसी फिल्मों में संवेदनशील रोबोट।

